Strategic Supplementation Case Study – Manbulloo Station, NT
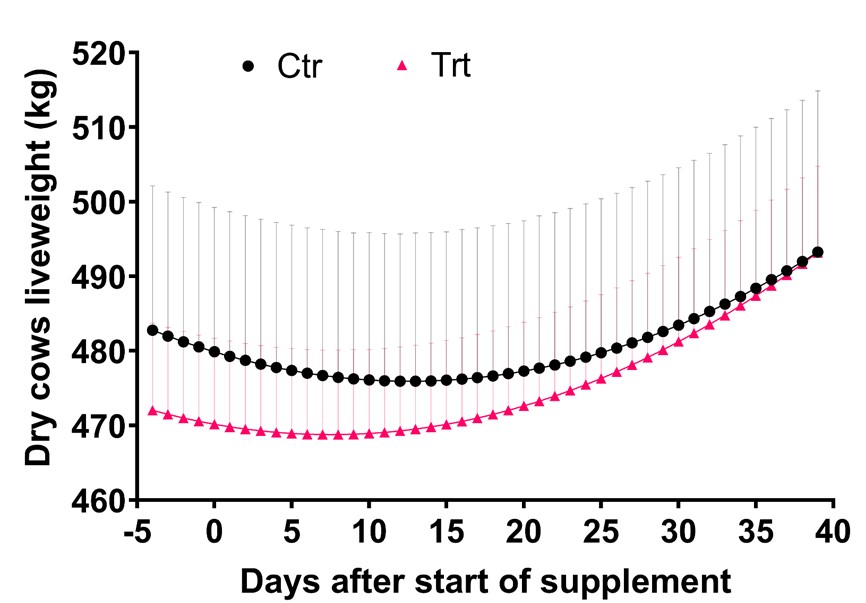
The trial conducted at Manbulloo Station, NT, revealed a significant effect of supplementation on live weight change in both wet and dry cows. Wet cows in the Control (Ctr) group lost 20kg during the first three weeks post-calving, while cows in the Treatment (Trt) group lost only 10kg. For dry cows, supplementing for 40 days increased their live weight (LW) by 21kg, compared to only 10kg in the Ctr group (Silva et al. 2023).
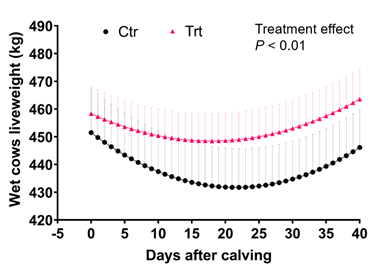
Figure 1. Impact of supplementation on LW change of lactating cows post calving. Manbulloo Station, NT
Figure 2. Impact of supplementation on LW change of dry cows post introduction. Manbulloo Station, NT
Further research and economic data analysis is required; however, if this difference persists, likely saleable weight will outweigh the supplementation costs.
Attendance of animals at the WoW-A
Daily attendance of study animals was recorded at the Manbulloo WoW-A (walk-over-weight and autodrafter). The initial high attendance was attributed to the lack of surface water elsewhere in the paddock. As the wet season started, cows were less motivated to frequent the WoW-A. While both the Crt and Trt groups had access to a mineral supplement external to the Wow-A, on average, 17.8% higher attendance was observed for the Trt group (P<0.01), with ~33% and 15% of cows with daily attendance for the treatment and control group, respectively (McCosker et al. 2023).
The results highlight the challenges associated with conducting in-paddock comparisons during a wet season. Additionally, it emphasises the influence of a highly palatable diet and the occurrence of presentation at the WoW-A.
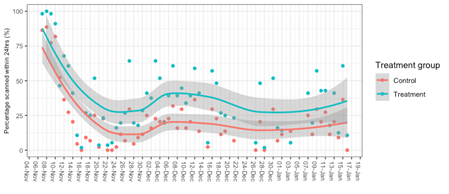
Figure 3. Attendance of study animals at walk-over-weighing and auto-drafter
Conclusion
To ensure the sustainability and profitability of the northern beef industry, the results highlight the need for better nutrition in breeding herds and, ultimately, the flexibility to make management decisions based on environmental conditions.
This project is funded by Meat and Livestock Australia and supported by the University of Queensland, Queensland Alliance of Agriculture and Food Innovation, Queensland Department of Agriculture and Fisheries, Northern Breeding Business, Northern Territory Government Department of Industry, Tourism and Trade and Feedworks.